

Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses. It is often caused by bacterial (germ) infection. Sometimes, viruses and fungi (molds) cause it. People with weak immune systems are more likely to develop bacterial or fungal sinusitis. Some people with allergies can have "allergic fungal sinusitis." Acute sinus disease lasts three to eight weeks. Sinus disease lasting longer than eight weeks is considered chronic.
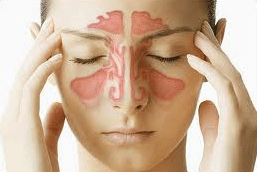
Nasal polyps are growths of mucosal tissue within the nose that can block nasal passagesor sinuses.Most nasal polyps start to grow near the ethmoid sinuses at and start to fill up empty space. Nasal polyps can grow large enough to block sinuses and the nasal airway, resulting in recurrent episodes of sinusitis and difficulty breathing through the nose.
According to the leading experts in immunology, when part of the immune system is either absent or not functioning properly, it can result in an immune deficiency disease. When the cause of this deficiency is hereditary or genetic, it is called a primary immunodeficiency disease (PIDD). Researchers have identified more than 150* different kinds of PIDD. The immune system is composed of white blood cells. These cells are made in the bone marrow and travel through the bloodstream and lymph nodes. They protect and defend against attacks by "foreign" invaders such as germs, bacteria and fungi.
Serious PIDDs typically become apparent in infancy. In milder forms, it often takes a pattern of recurrent infections before PIDD is suspected. In some cases, a PIDD is not diagnosed until people reach their 20s and 30s.