

Food allergy symptoms occur most often in babies and children but can appear at any age. Foods that you have eaten for years without problems can cause allergies. An allergy occurs when something causes your body's natural defenses to overreact. Some 40-50 million Americans have an allergy of some kind, but food allergies are rare. Up to 4 percent of adults have food allergies.
Some mild food allergy symptoms may be caused by a food sensitivity rather than an allergic reaction. An allergist can help determine if it is a true allergic reaction. Shellfish, peanuts and tree nuts are the most common food allergens for adults. Milk, eggs, soy, wheat, shellfish, peanuts and tree nuts are the most common food allergens for children. An allergic reaction to food, often called food allergies, can cause mild to serious symptoms such as:


If you suffer from hay fever and you've ever experienced an itchy mouth or scratchy throat after eating certain raw fruits or vegetables and some tree nuts, you may have oral allergy syndrome symptoms. Oral allergy syndrome, also known as pollen-food syndrome,is caused by cross-reacting allergens found in both pollen and raw fruits, vegetables, or some tree nuts. The immune system recognizes the pollen and similar proteins in the food and directs an allergic response to it. People affected by oral allergy syndrome can usually eat the same fruits or vegetables in cooked form because the proteins are distorted during the heating process, so that the immune system no longer recognizes the food. Oral allergy syndrome typically does not appear in young children; the onset is more common in older children, teens, and young adults who have been eating the fruits or vegetables in question for years without any problems. Those with oral allergy syndrome typically have allergy to birch, ragweed, or grass pollens.

Food intolerances differ from a food allergy, as the immune system is not involved when a person is intolerant to a food. Two common intolerances, lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance occurs when an individual's small intestine does not produce enough of the lactase enzyme. Therefore, affected individuals are not able to digest lactose, a type of sugar found in dairy products. The symptoms of lactose intolerance typically occur within 30 minutes to 2 hours after ingesting dairy products. Large doses of dairy may cause increased symptoms.The lack of lactase enzyme causes abdominal gas, diarrhea and abdominal cramping.
An adverse reaction to gluten is known as celiac disease or "celiac sprue". This disease requires a lifelong restriction of gluten, which is found in wheat, rye, and barley, and perhaps oats. These grains and their by-products must be strictly avoided by people with celiac disease.Celiac disease causes damage to the lining of the small intestine, which prevents the proper absorption of nutrients in foods. This is turn can cause a person with Celiac disease to become malnourished.Celiac disease can cause many symptoms, including bloating and gas, diarrhea, constipation, headaches, itchy skin rash, and pale mouth sores, to name a few. The symptoms may vary amongst affected individuals.
Eosinophilic esophagitis, also known as EE or EoE, is an allergic inflammatory disease and typically chronic disorder that affects from one to four of every 10,000 people in the United States. It is a recently recognized disease with increasing diagnoses, resulting in part from growing awareness of the condition. An estimated 50 percent of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis also have seasonal allergies or asthma. Many others also have food allergies or eczema. Some patients note a seasonal flare up of the condition, typically in the spring and in the summer.
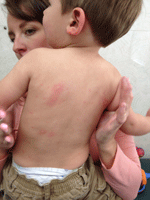
Anaphylaxis and throat swelling is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. This serious reaction happens within seconds to minutes after you take the drug, bee sting or food allergy. With this type of reaction:
Laryngeal Edema (Throat Swelling)
